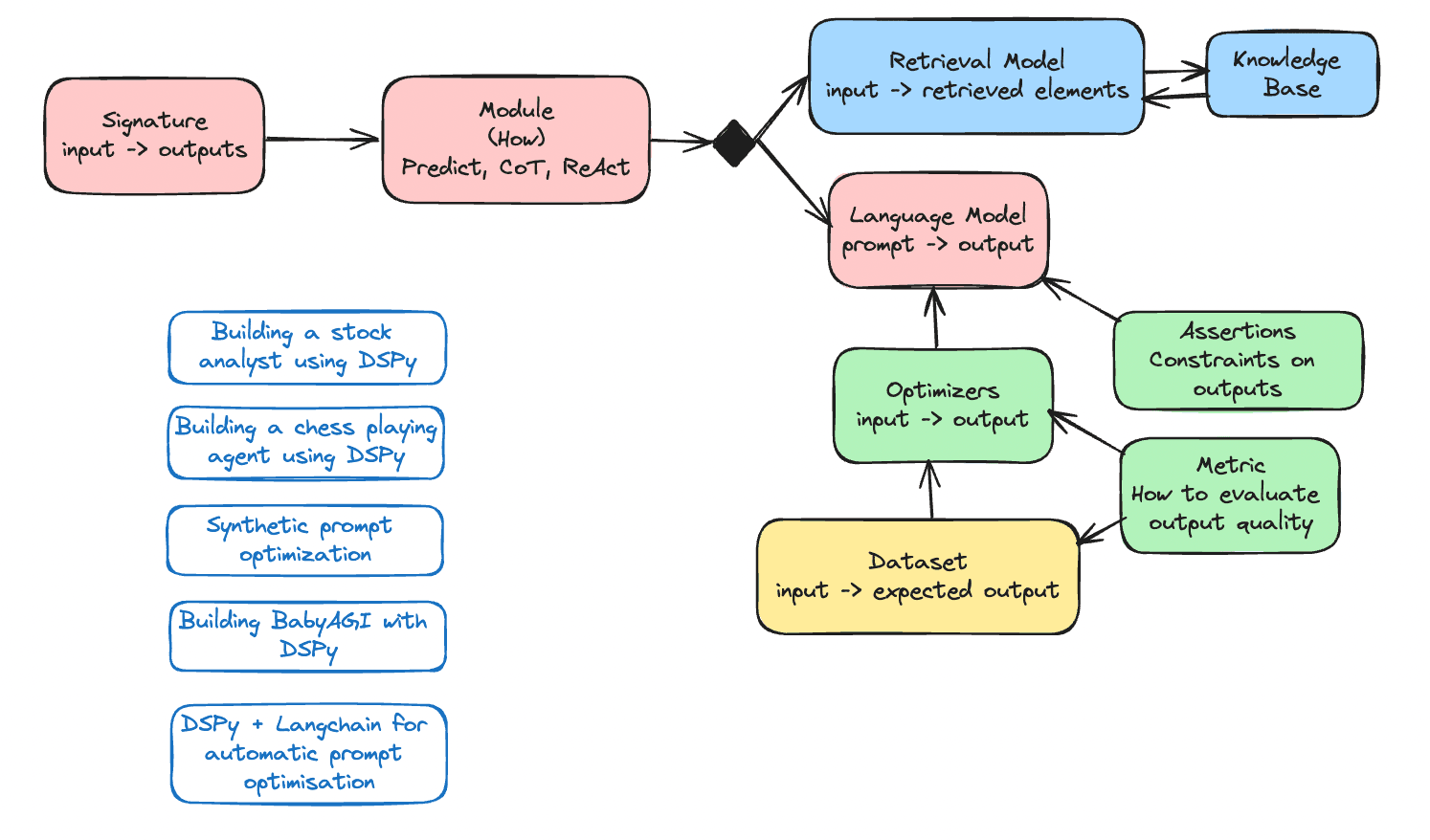
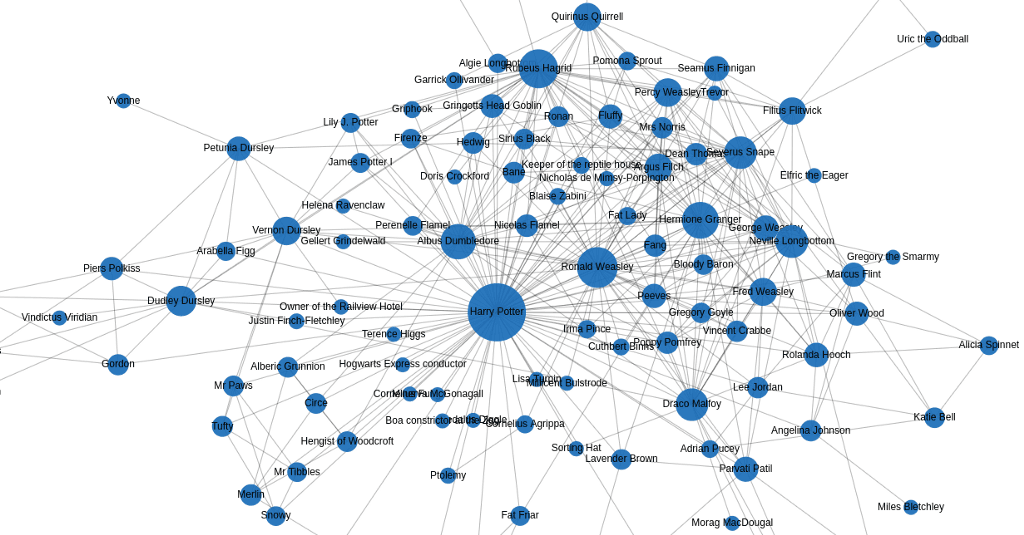
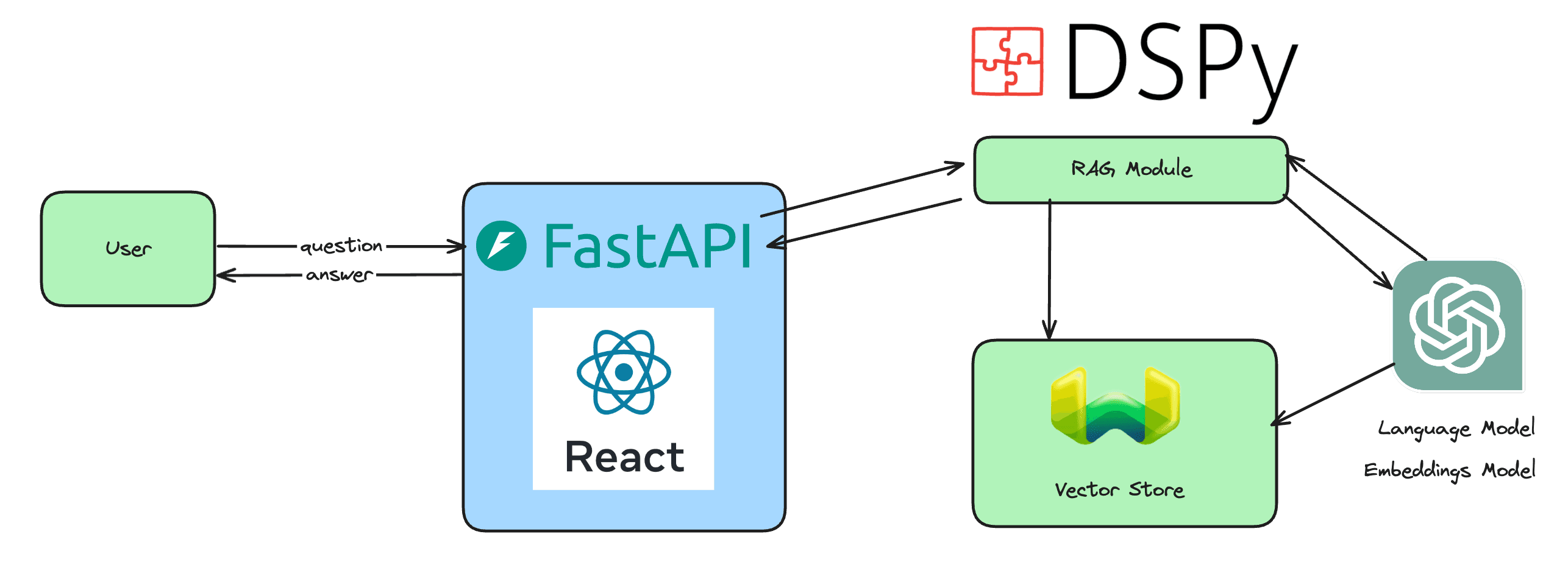
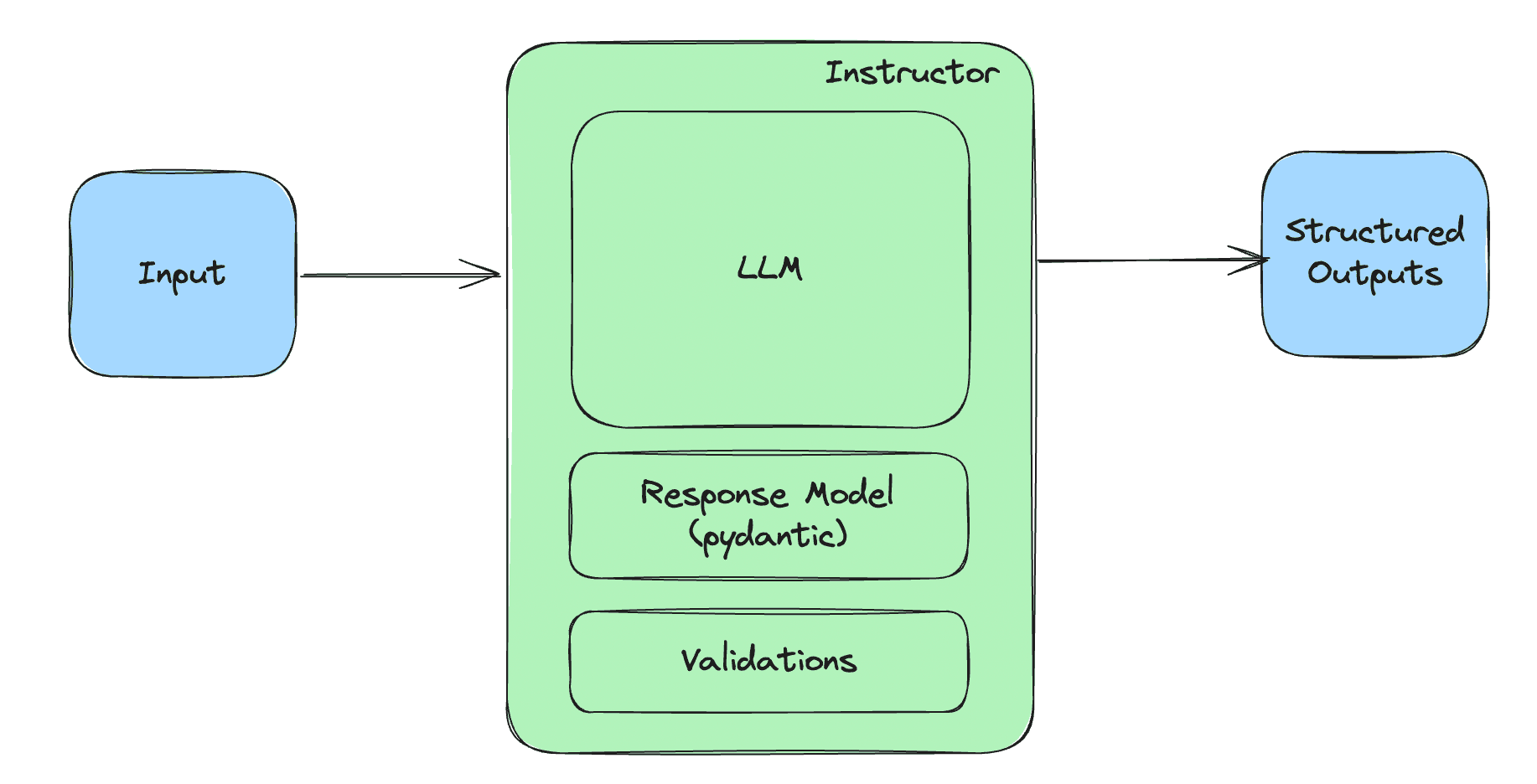
OpenAI's ChatGPT has become a pivotal tool in the generative AI landscape, not just as a product for consumer use, but as a sophisticated data acquisition mechanism that gives the company a strategic advantage over competitors. While many in the tech world are still searching for the "killer app" in the AI space, some industry insiders argue that ChatGPT itself may already hold that distinction, thanks to its unique human-in-the-loop design and its ability to gather vast amounts of user interaction data.
Data as a Strategic Asset
One of the key aspects of OpenAI's success lies in its ability to gather real-time feedback from its users, who number over 200 million worldwide. This user base provides a steady stream of conversational data that helps refine the language model and improve its performance over time. According to industry experts, this is part of OpenAI's broader data acquisition strategy, positioning the company as a leader in a highly competitive market.
“The scale of OpenAI’s data collection through free access to ChatGPT cannot be understated,” said one AI analyst. "Every interaction, even if not explicitly rated by the user, contributes to the model’s ongoing improvement. The model can learn from the flow of conversation, detecting when an answer was accepted or when the user continued to probe further."
This feedback loop is facilitated through the chat interface, which allows users to ask questions, iterate on responses, and refine their queries. While OpenAI has mechanisms in place for users to provide explicit feedback—such as thumbs-up or thumbs-down ratings—the majority of the system's learning happens through less obvious cues, such as follow-up questions or the length of interactions. The company then uses this information to fine-tune its models and implement reinforcement learning from human feedback (RLHF).
Leveraging Trillions of Tokens
OpenAI reportedly processes over a billion tasks per month, which includes approximately two trillion tokens—units of text used to represent words and phrases. This vast volume of interactions allows OpenAI to gather a wealth of tacit knowledge from its users, essentially crowdsourcing feedback on a massive scale. As users engage in more complex, multi-turn conversations with the AI, the model can better understand context, anticipate user needs, and refine its output.
The company’s data collection approach goes beyond simple text generation. By engaging in iterative, back-and-forth conversations with users, OpenAI’s language models effectively perform real-world testing. When users ask follow-up questions or modify their requests, the system can assess which suggestions worked and which did not, even without explicit feedback. According to AI researchers, this type of conversational feedback is invaluable in improving the model’s reliability and reducing instances of "hallucinations"—when the AI generates inaccurate or misleading information.
ChatGPT: The “Killer App”?
Many experts believe that ChatGPT may already be the "killer app" in the generative AI field. While there has been significant interest in integrating large language models (LLMs) into various business applications—such as automating text-to-SQL queries or augmenting data analytics workflows—most implementations still rely heavily on human oversight to ensure accuracy. As a result, the chat interface remains the most suitable format for widespread use, particularly in cases where iterative refinement is necessary.
“Despite all the hype around new AI tools, the core strength of LLMs like ChatGPT is their ability to iterate on user input quickly and effectively,” said another industry insider. “This is especially important given the tendency of AI systems to hallucinate or make errors in complex queries. In a chat-based system, users can catch these errors and correct them in real time.”
Monetization and Long-Term Strategy
While ChatGPT is free for many users, some experts argue that this is only a stepping stone toward OpenAI's broader monetization strategy. The company already offers premium services through its API, which is widely used by developers and businesses for custom applications, fine-tuning models, and integrating AI into larger systems. In addition, OpenAI has been exploring other business models, including potential ad-based revenue streams.
According to insiders, OpenAI is playing a long game. By offering free access to a powerful language model, the company is able to attract a large user base, which in turn helps to gather more data, improve the model, and create a network effect that makes its platform even more valuable over time.
Challenges Ahead
Despite these advantages, OpenAI faces challenges in ensuring the reliability and trustworthiness of its models. Hallucinations remain a significant concern, particularly in use cases that require precise, fact-based outputs, such as generating SQL queries or conducting data analytics. Some users have expressed skepticism about whether OpenAI's feedback mechanisms can reliably discern useful from useless output, especially in cases where users continue to interact with the model even after receiving incorrect answers.
"While OpenAI’s data acquisition strategy is impressive, it’s not without its limitations,” said one AI ethics expert. “Relying on user behavior to evaluate the quality of responses introduces potential biases. If users don’t provide explicit feedback, the model may have a hard time distinguishing between a good conversation and one that’s simply long or repetitive."
As the generative AI space continues to evolve, OpenAI’s ability to harness user feedback at scale could prove to be its defining competitive advantage. Whether ChatGPT is truly the “killer app” remains to be seen, but for now, it has cemented itself as a powerful tool for both consumers and businesses, while simultaneously serving as a data engine driving the future of AI.