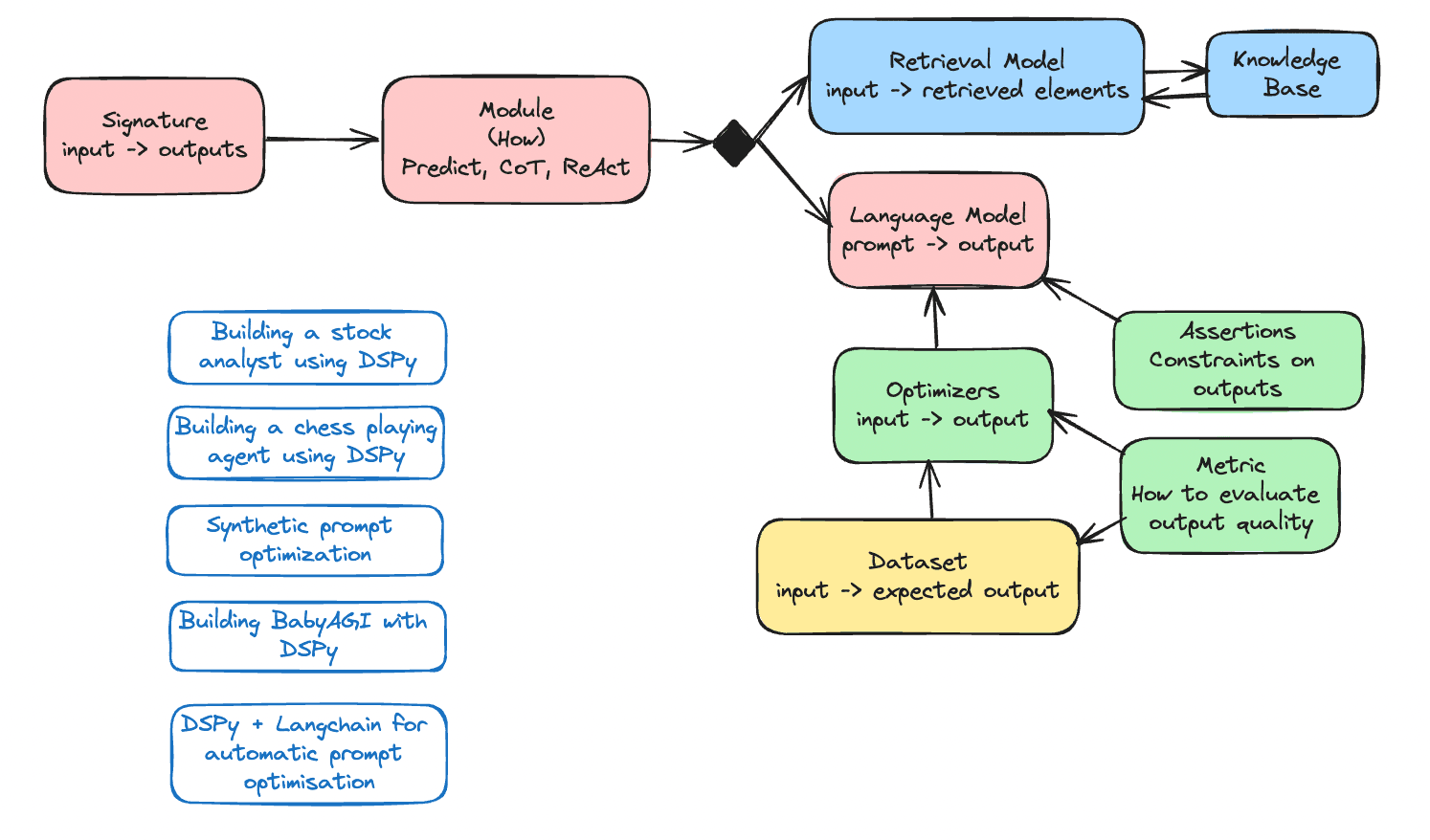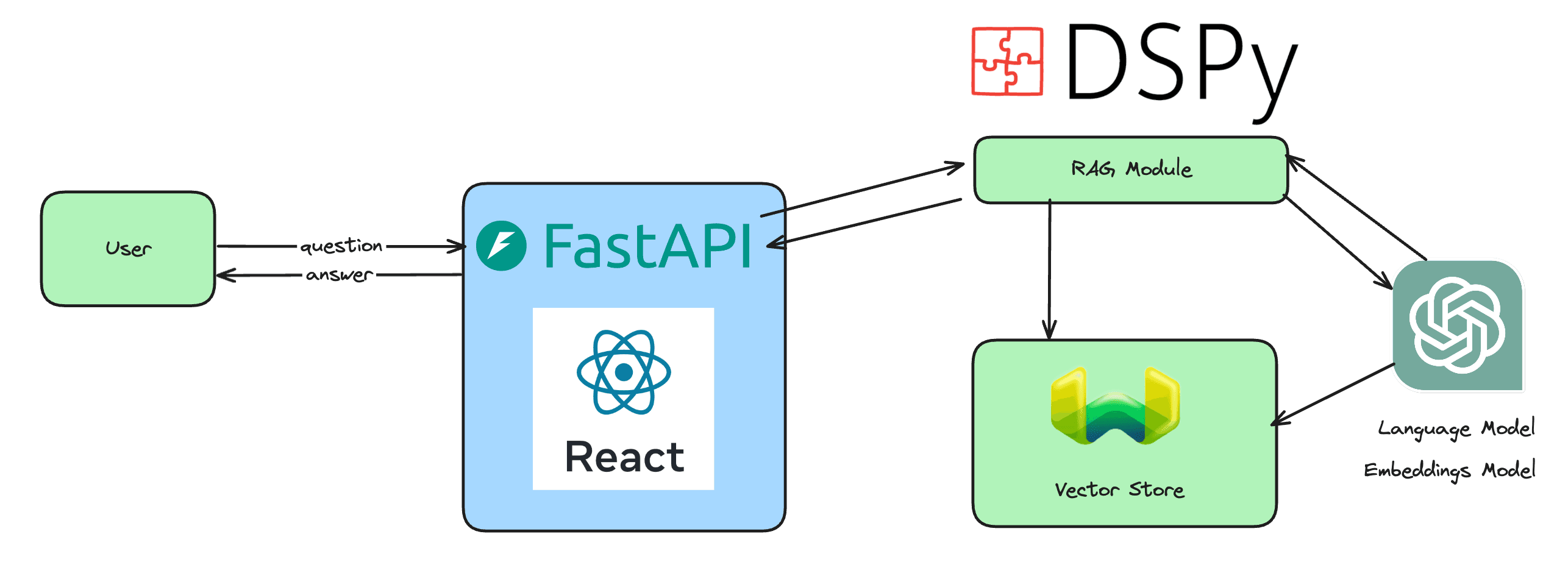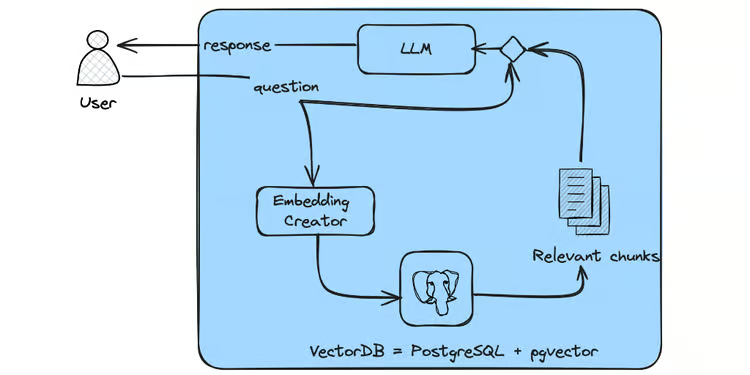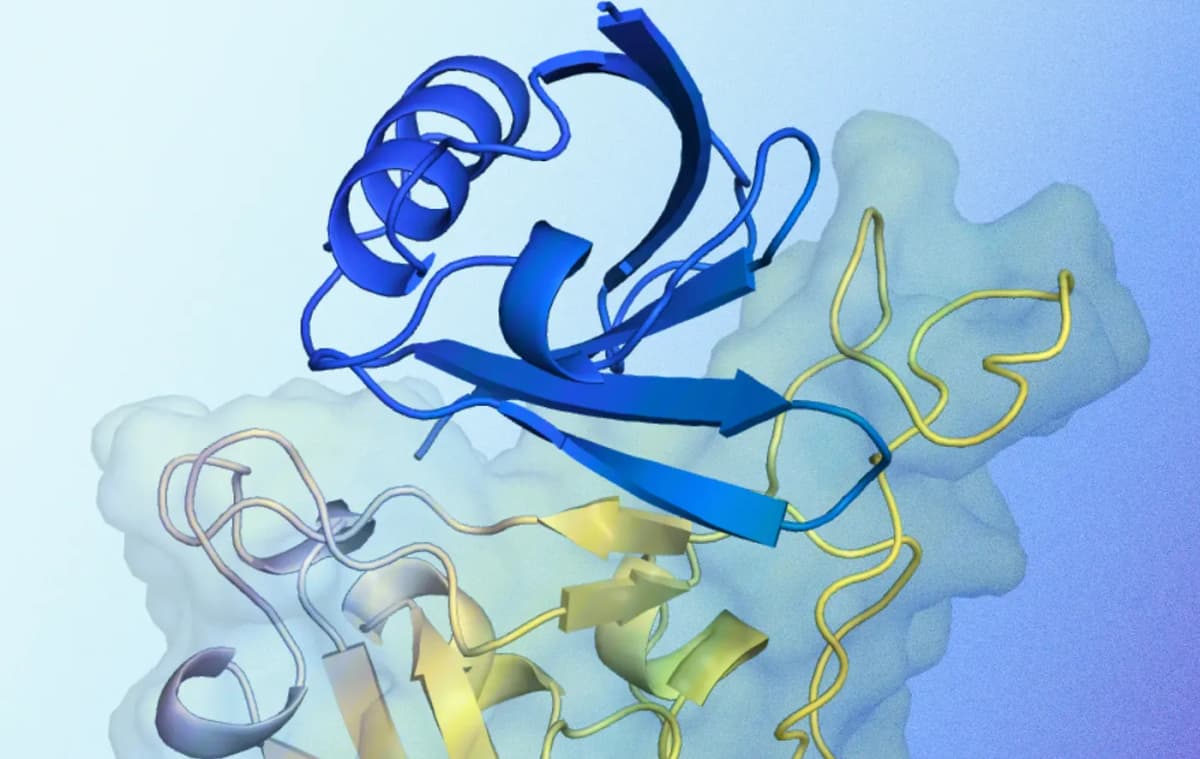
In a significant leap for biological and health research, Google DeepMind announced AlphaProteo, a new AI-driven system designed to create novel protein binders with potential to revolutionize drug development, disease research, and biosensor development. Building on the success of AlphaFold, which predicts protein structures, AlphaProteo goes further by generating new proteins that can tightly bind to specific targets, an essential aspect of many biological processes.
AlphaProteo has demonstrated remarkable results across seven tested target proteins, including the SARS-CoV-2 spike protein and VEGF-A, a protein associated with cancer and diabetes complications. The AI system has achieved 3 to 300 times better binding affinities than traditional methods, which rely on labor-intensive lab work and trial-and-error optimization.
The system's success is underpinned by extensive training on data from the Protein Data Bank and AlphaFold predictions. By inputting the structure of a target molecule and desired binding sites, AlphaProteo generates potential protein binders, some of which have been experimentally validated to outperform existing methods.
However, AlphaProteo still faces challenges. For example, it struggled to design successful binders for TNFα, a protein linked to autoimmune diseases like rheumatoid arthritis, underscoring areas for improvement.
DeepMind emphasizes the responsible development of this technology, highlighting its collaboration with biosecurity experts to mitigate risks. Moving forward, the team plans to collaborate with the scientific community, improve the system's performance, and explore drug design applications with Isomorphic Labs. AlphaProteo represents a promising step toward advancing biological research and therapeutic development.